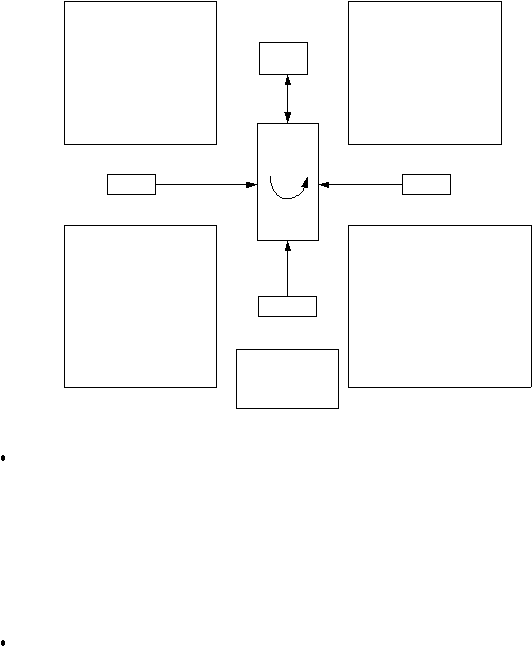
11
op®ietary
Entry barriers
Economies of Scale
Prop®ietary
product differences
Brand identity
Switching costs
Capital requirements
Access to distribution
Absolute cost advantage
Proprietary
curve
Access to necessary inputs
Proprietary
low-cost product design
Government policy
Expected retaliation
New
Entrants
Threat of
New
Entrants
Industry
Competitors
Rivalry Determinants
Industry Growth
Fixed (or storage) costs / value added
Intermittent overcapacity
Product differences
Brand Identity
Switching costs
Concentration
and balance
Informational
complexity
Diversity of competitors
Corporate stakes
Exit barriers
Supplier
Bargaining Power
Bargaining Power
of Suppliers
of buyer
Buyer
Determinants of Supplier Power
Intensity of
Rivalry
Determinants of Buyer Power
Differentiation of inputs
Switching costs of suppliers and firms
in the industry
Presence of substitute inputs
Supplier concentration
Importance of colume to supplier
Cost relative to total purchases in the
industry
Impact of inputs on cost or
differentiation
Threat of forward integration relative
to threat of backward integration by
firms in the industry
Threat of
Substitues
Substitutes
Determinants of
Substitution Threat
Relative price
performance of substitute
Switching costs
Buyer propensity to
substitute
Bargaining
Leverage
Buyer concentration
versus firm
concentration
Buyer volume
Buyer switching costs
relative to firm
switching costs
Buyer information
Ability to backward
integrate
Substitute products
Pull-through
Price Sensitivity
Price/total purchase
Product differences
Brand identity
Impact on quality or
performance
Buyer profits
Decision makers’
incentives
Figure 2.1. Forces Driving Industry Competition
Threat of entry
The seriousness of the threat of entry depends on the barriers present and on the
reaction
from existing competitors that the entrant can expect. If barriers
to entry
are
high
and
a
newcomer
can
expect
sharp
retaliation
from the
entrenched
competitors, he or she obviously will not pose a serious threat of entering.
Powerful suppliers
Suppliers exert bargaining
power on participants
in an
industry by
raising prices
or
reducing
the
quality
of
purchased
goods and services. Powerful suppliers
thereby, can squeeze profitability out of an industry unable to recover cost
increases in its own prices.